SOUND SENSOR
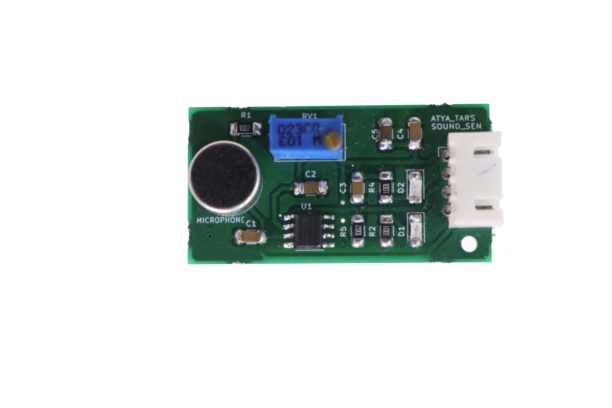
General Description:
A sound sensor is a device that converts sound waves into electrical signals that can be processed by an electronic circuit. They can be used to detect and measure the frequency and amplitude of sound waves.
Working Principle:
The working principle of a sound sensor is based on the conversion of sound waves into an electrical signal. When sound waves strike a microphone, they cause the diaphragm to vibrate. This vibration generates an electrical signal that is proportional to the amplitude of the sound waves. This electrical signal is then sent to an electronic circuit for processing.
Specifications:
1. Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
2. LM393 comparator with threshold preset
3. Induction distance: 0.5 Meter
4. Operating current: 4~5 mA
5. Microphone Sensitivity (1kHz): 52 to 48 dB
6. Easy to use with Microcontrollers or even with normal Digital/Analog IC
7. Small, cheap, and easily available
Requirements
| S. No. | Component Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LM393(OP-AMP) | |
| 2 | Resistors | 150R,1k,10k(2),100k(2) |
| 3 | Potentiometer (adjustable) | 10k |
| 4 | LED'S | |
| 5 | Microphone | |
| 6 | Male pin connector | 4 |
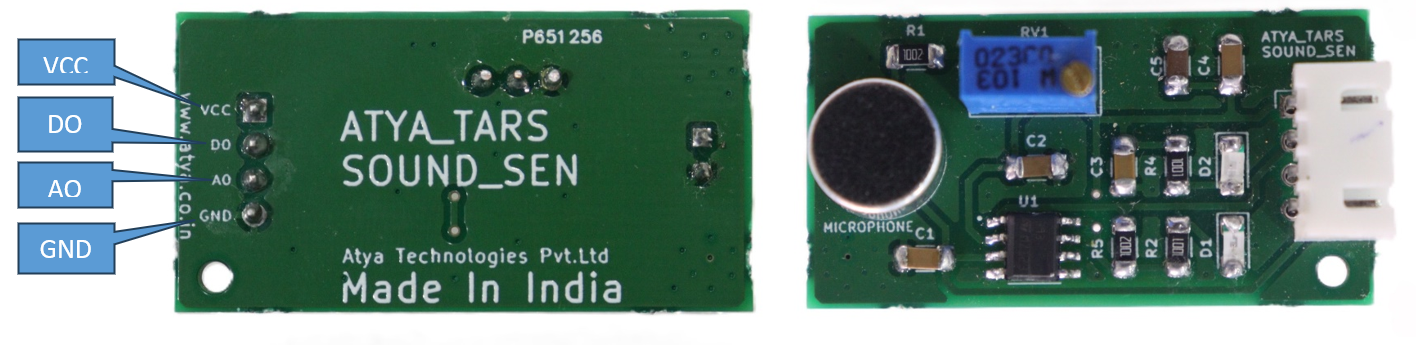
Pin configuration:
| S. No. | Pins | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A0 | Analog output pin |
| 2 | GND(G) | Connect to ground |
| 3 | VCC (+) | 3.3 - 5 v |
| 4 | D0 | Digital output pin |
Pin Diagrams:
Applications:
1. Hearing aids
2. Telephones
3. Tape recorders and karaoke
4. Live and recorded audio engineering
5. Radio and television broadcasting
6. Speech recognition technology


