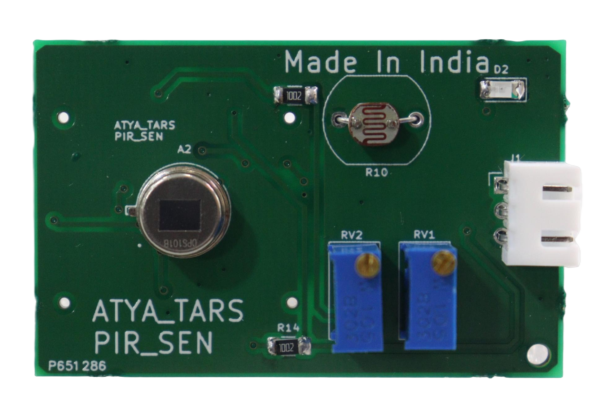
PIR SENSOR

General Description:
PIR (Passive Infrared) sensors detect infrared radiation emitted by heat sources like people or animals, despite being invisible to humans. Often termed 'motion detectors,' they sense movement by detecting changes in infrared wavelengths. Equipped with a pyroelectric sensor, PIR sensors measure varying levels of infrared radiation emitted by objects. Unlike active sensors, they do not emit energy but only detect it. When motion occurs within the sensor's range, it triggers a positive change; when motion stops, it triggers a negative change, enabling motion detection.
Working Principle:
Passive Infrared sensors do not emit energy into space. Instead, they receive infrared radiation from objects, particularly the human body, to initiate an alarm. Objects with a temperature above absolute zero consistently radiate infrared rays into their surroundings. The human body, with a surface temperature between 27°C and 36°C, emits most of its radiant energy in the wavelength range of 8 μm to 12 μm.
Within the detection area, the PIR sensor's lens captures infrared radiation emitted by the human body, even though clothing focuses it on the pyroelectric sensor. When a human body enters and exits the sensor's view, the pyroelectric sensor detects temperature changes, generating an alarm signal. Specifications:
Specifications:
1. Operating voltage varying from 4.5 V to 20 V
2. Output voltage is High/Low (3.3V TTL).
3. Can distinguish between object movement and human movement
4. Has to operating modes - Repeatable(H) and Non- Repeatable (NH)
5. Cover distance of about 120° and 7 meters
6. Average current consumption of 0.06 mA
7. Operating temperature from -20° to +80° Celsius
8. Sensing range extends up to 7 meters
Requirements
| S. No. | Component Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BISS0001 CHIP | |
| 2 | 3V DC Regulator | |
| 3 | Retrigger Setting Jumper | |
| 4 | Pyroelectric Sensor | |
| 5 | Fresnel Lens | |
| 6 | Time Delay Adjust | |
| 7 | Sensitivity Adjust | |
| 8 | Resistors | 10k, 18k, 47k, 1M, 2k, 6.8k, 470k |
| 9 | Capacitors | 47μ, 103, 22μ, 104, 502 |
| 10 | Male Connector | 3 |
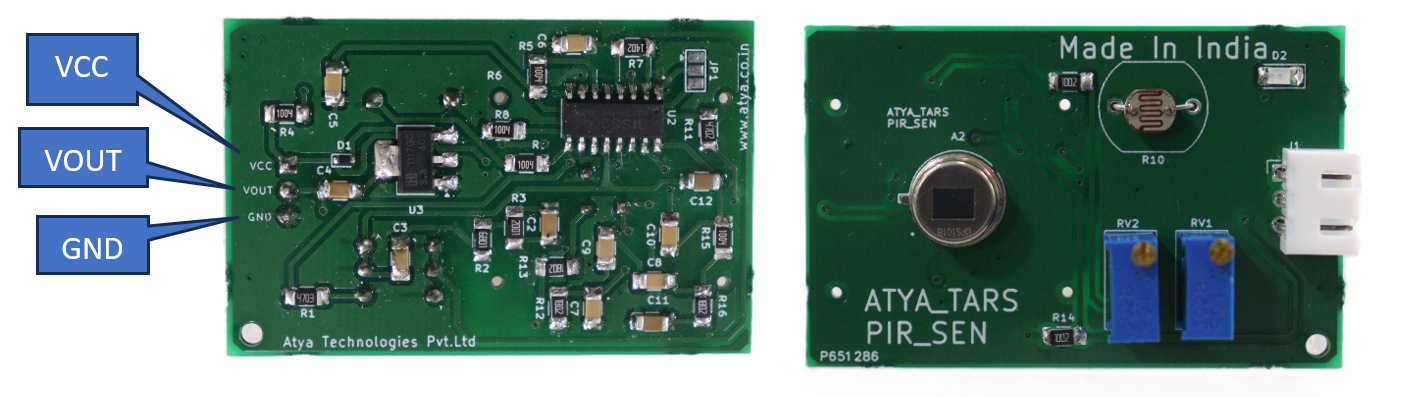
Pin configuration:
| S. No. | Pins | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | The input voltage is +5V for typical applications. Can range from 4.5V- 20V |
| 2 | High/Low Output (Dout) | Digital pulse high (3.3V) when triggered (motion detected) digital low(0V) when idle (no motion detected) |
| 3 | Ground | Connected to the ground of the circuit |
Pin Diagrams:
Applications:
1. Switch
2. Motion sensor
3. Thief-guarding system
4. Industrial automation
5. PIR sensors are used in thermal sensing applications, such as security and motion detection.
6. The IR Sensor can be used in IP cameras.
7. Used for Alarm systems and other crime-prevention devices.
For more info: Refer the Datasheets!
MOTION DETECTION SENSOR
General Description:
A passive infrared sensor is an electronic sensor that measures infrared light radiating from objects in its field of view. They are most often used in PIR-based motion detectors. PIR sensors are commonly used in security alarms and automatic lighting applications. Technically, PIR is made of a pyroelectric sensor, which can detect different levels of infrared radiation. For example, everything emits varying levels of radiation, and the level of radiation will increase with the increase of the object's temperature.
Working Principle:
The PIR Sensor is pretty complicated when compared to the other sensors. The PIR Sensor has 2 slots, and the slots are made of sensitive material. When the sensor is inactive, then the two slots will sense the same amount of IR. The ambient amount radiates from the outdoors, walls or rooms, etc.
When a human body or any animal passes by, it intercepts the first slot of the PIR sensor. This causes a positive differential change between the two bisects. But when the body leaves the sensing area, the sensor generates a negative differential change between the two bisects.
Specifications:
1. The supply voltage range is 3.3 V to 5 V.
2. Working current ranges from 12 to 20 mA.
3. Sensitivity is adjustable within the range of 120 to 530 μV.
4. Maximum detecting range is 2 meters at 25 ℃.
5. Sensor chip model: S16-L221D.
6. low power consumption.
7. Compact size
8. Considered cost-effective for various applications.
Requirements
| S. No. | Component Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Voltage Regulator (XC6206P302) - 3.3V | |
| 2 | S16-L221D (PIR sensor) | |
| 3 | Capacitors | 10 µF, 100nF, |
| 4 | Resistors | 4.7k, 1M, 39k |
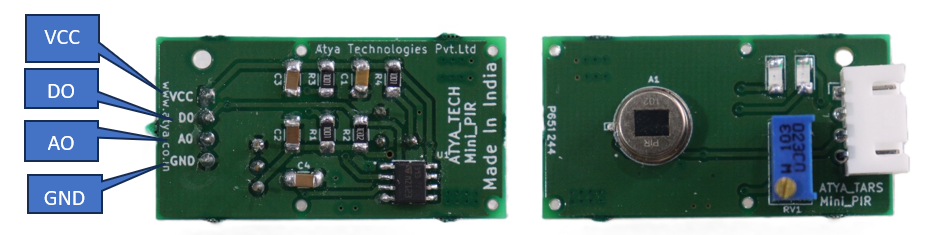
Pin configuration:
| S. No. | Pins | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Connect to the ground |
| 2 | VCC | Connect to 3.3v to 5V |
| 3 | NC | No Connection |
| 4 | REL | Connect to Digital Output |
Pin Diagrams:
Applications:
1. Home and Business Security Systems
2. Automatic Lighting Systems
3. Industrial Machinery Monitoring
4. Structural Health Monitoring
5. Aerospace Industry
6. Security Alarm System
7. Human Detection System
For more info: Refer the Datasheets!
IR TRANSCEIVER
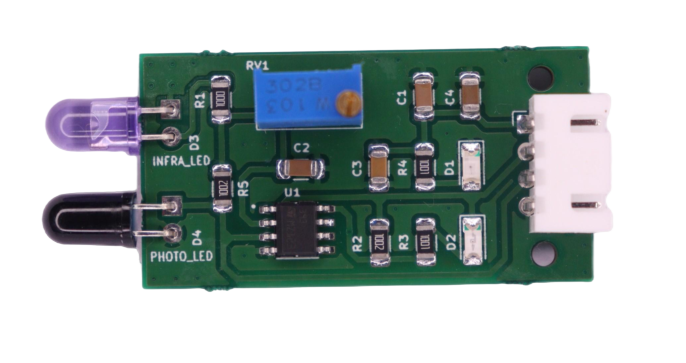
General Description:
An IR sensor can measure the heat of an object as well as detect the motion. There are two types of IR sensors. They are:
Active Infrared Sensor: Active infrared sensors consist of two elements: an infrared source and an infrared detector. Infrared sources include the LED or infrared laser diode. Infrared detectors include photodiodes or phototransistors. The energy emitted by the infrared source is reflected by an object and falls on the infrared detector.
Passive Infrared Sensors: They are of two types: quantum and thermal. Thermal infrared sensors use infrared energy as the source of heat. Thermocouples, pyroelectric detectors, and bolometers are the common types of thermal infrared detectors. Quantum-type infrared sensors offer higher detection performance. It is faster than thermal-type infrared detectors. The photo sensitivity of quantum-type detectors is wavelength- dependent.
Working Principle:
There are different types of infrared transmitters depending on their wavelengths, output power and response time. An IR sensor consists of an IR LED and an IR Photodiode, together they are called as PhotoCoupler or OptoCoupler.
IR Transmitter or IR LED:Infrared Transmitter is a light-emitting diode (LED) which emits infrared radiations called as IR LED's. Even though an IR LED looks like a normal LED, the radiation emitted by it is invisible to the human eye.
 IR Receiver or Photodiode
IR Receiver or Photodiode
Infrared receivers or infrared sensors detect the radiation from an IR transmitter. IR receivers come in the form of photodiodes and phototransistors. Infrared Photodiodes are different from normal photodiodes as they detect only infrared radiation.

Different types of IR receivers exist based on the wavelength, voltage, package, etc. When used in an infrared transmitter-receiver combination, the wavelength of the receiver should match that of the transmitter.
The emitter is an IR LED and the detector is an IR photodiode. The IR photodiode is sensitive to the IR light emitted by an IR LED. The photo-diode resistance and output voltage change in proportion to the IR light received. This is the underlying working principle of the IR sensor.

When the IR transmitter emits radiation, it reaches the object and some of the radiation reflects to the IR receiver. Based on the intensity of the reception by the IR receiver, the output of the sensor is defined.
Specifications:
1. The main chip of the sensor is LM393.
2. It operates at an operating voltage of 3.6 to 5 volts.
3. The average current consumption of the sensor is 0.06 mA.
4. The detection angle of the sensor is 35 degrees.
5. The distance measuring range of the sensor is 2 to 30 cm.
Requirements
| S. No. | Component Name | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IC - LM393 (Op-Amp) | |
| 2 | Photodiode | |
| 3 | IR Sensor | |
| 4 | Resistor | 100R,330R,10K |
| 5 | Potentiometer | 10K |
| 6 | Male Connectors | 3 |
Pin configuration:
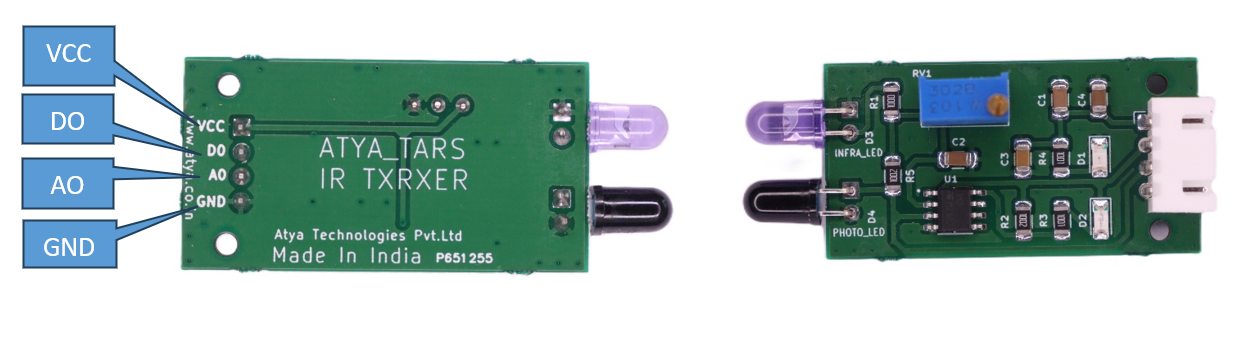
| S. No. | Pins | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Input Voltage: 3.3-5v |
| 2 | GND | Connect to ground |
| 3 | OUT | Digital output pin |
Pin Diagrams:
Applications:
1. Night Vision Devices
2. Radiation Thermometers
3. Infrared Tracking
4. IR Imaging Devices




